
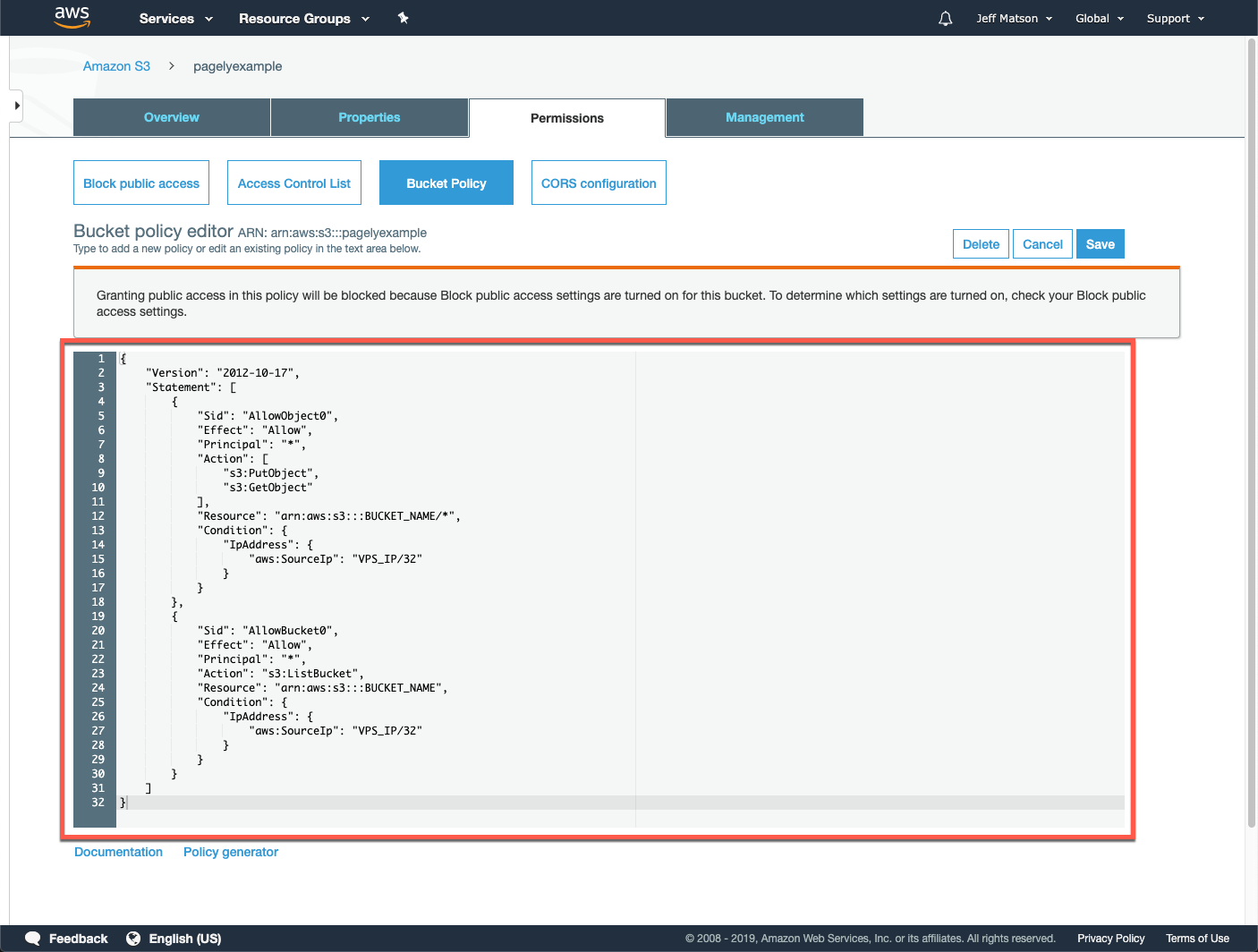
Outline roles that cover the access needs of users and objects. Website: You may configure the bucket for static website hosting. Versioning: Versioning assists you when recovering accidental deletes and overwrites. Transfer acceleration leverages the globally distributed edge locations via Amazon CloudFront. Transfer acceleration: Transfer acceleration enables easy, secure and fast movement of files over extended distances between your S3 bucket and your client. AWS shows the tags on your charges allocation report, with costs and usage aggregated via the tags. This can help you track and organize your costs on S3. Tagging: This setting allows you to add tags to an S3 bucket. This setting lets the bucket creator pass on the cost of downloading data from the bucket to the account downloading the content. RequestPayment: By default, the AWS account that sets up a bucket also receives bills for requests made to the bucket. Replication: This option lets you automatically copy the content of the bucket to additional buckets, within the Amazon Region. ACL and bucket policies are two ways to grant permissions for an entire bucket. Policy and ACL (access control list): Both buckets and the objects stored within them are private, unless you specify otherwise. You may also wish to configure a default period of retention and mode that applies to the latest objects that are uploaded to the bucket. Object locking: Enables the object lock feature for a bucket. All access log records give details regarding one access request, including bucket name, requester, request action, request time, error code, and response status. Logging: Logging lets you monitor requests for access to the bucket. Amazon S3 retains these details in the location subresources and offers an API so you can gain access to this information. Location: When you establish a bucket, you choose the AWS Region where you want Amazon S3 to develop the bucket. Lifecycle: You may specify lifecycle regulations for objects within your bucket that feature a well-outlined lifecycle. Below lists subresources that let you oversee bucket-specific configurations.Ĭors (cross-origin resource sharing): You may configure your bucket to permit cross-origin requests.Įvent notification: You may permit your bucket to alert you of particular bucket events. These are known as subresources since they function in the context of a certain object or bucket. You may also utilize the AWS SDKs or the console. You can employ the Amazon S3 API to manage and develop these subresources. Amazon S3 offers support for subresources so you can manage and retain the bucket configuration details. S3 Transfer Acceleration can assist with the execution of secure and fast transfers from the client to an S3 bucket via AWS edge locations.Īmazon S3 provides support for different alternatives for you to configure your bucket. Similarly, when creating a bucket, a user can establish server access logs, tags, object-level API logs, and encryption. This may help stop IT specialists from accidentally deleting an object. An IT specialist may enable different versions for S3 buckets to retain every version of an object when an operation is carried out on it, for example a delete or copy operation. S3 Bucket Configuration: Understanding SubresourcesĪWS provides various tools for Amazon S3 buckets. You can optionally enable the Object Lock feature in Advanced settings > Object Lock. In Bucket settings for Block Public Access, specify if you want to allow or block access from external networks.Ħ. Keep in mind there are special charges for moving objects outside a region.ĥ. Select a Region near you to keep latency and cost to a minimum and to address regulatory demands. The bucket name must be unique, begin with a number or lowercase letter, be between 3-63 characters, and may not feature any uppercase characters.Ĥ. In Bucket name, create a DNS-accepted name for your bucket.Learn more in our guide to S3 pricingĭeveloping an S3 bucket via the S3 console: Keep in mind that buckets are priced according to data volume stored in them, and other criteria. S3 lets you create buckets using the S3 Console or the API. According to the default settings, you can have as many as 100 buckets for each AWS account. You may upload as many objects as you like to the bucket. The AWS account that opened the bucket remains the owner. Once you have configured a bucket, you can’t modify the Region or bucket name. You may also wish to select additional storage management choices for your bucket. I have created an s3 bucket in aws and added the correct permissions and user group etc.Before you can store content in S3, you need to open a new bucket, selecting a bucket name and Region.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
